low flow low gradient aortic stenosis guidelines
However as many as 30 of patients who have a calculated AVA in the severe range have other parameters suggesting mild or moderate disease ie mean gradient low-flowlow-gradient AS LFLGAS may truly have severe AS with resultant myocardial failure true AS or may have more moderate degrees of AS and. The severity of low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis cases continue to be misunderstood because of challenging diagnosis and treatment remains complex.

The Challenge Of Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Patrick T O Gara Youtube
We discuss current diagnostic and treatment modalities for low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis.

. Low-flow low-gradient severe aortic stenosis AS is characterised by a small aortic valve area AVA and low mean gradient MG secondary to a low cardiac output and may occur in patients with either a preserved or reduced left ventricular ejection fraction LVEF. With this hemodynamic presentation it is difficult to distinguish true aortic valve stenosis where the primary Author. A squared function of flow and may thus be pseudo-normalized and underestimate stenosis severity in presence of low flow.
Highlights in this focused update on aortic stenosis document include. LF LG AS is characterized by combination of severe aortic valve stenosis calculated aortic valve area AVA low transvalvular gradient mean gradient low flow stroke volume 35 mlm 2. Low gradient low flow aortic stenosis is defined by a left ventricular ejection fraction 40 mean gradient 30 mm Hg and effective orifice area 10 cm 2.
Important is to note that gradients are a. 1 When a severe AS becomes symptomatic the rate of death is 50 at 2 years unless valve replacement is performed. Normal flow low gradient aortic stenosis med bevarad vänsterkammar-EF- Medelgradient 50 SVi 35mlm 2.
Severe aortic stenosis AS is usually defined on the basis of both an aortic valve effective orifice area EOA 10 cm 2 and a mean transvalvular gradient 40 mm Hg 1 2Nonetheless given that gradients are a squared function of flow even a modest decrease in flow may lead to an important reduction in gradient even if the stenosis is very severe. Affiliation 1 Section of Cardiology. New classification of AS by gradient flow and ejection fraction.
Care From the 1 Heart Program In the Nation is Closer Than You Think. Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis with normal and depressed left ventricular ejection fraction. Aortic valve replacement for low-flowlow-gradient aortic stenosis operative risk stratification and long-term outcome.
About 60 of patients with paradoxical low-flow low-gradient PLF-LG aortic stenosis AS have a severe disease that justifies aortic valve replacement AVR. High gradient severe AS The 2020 American Heart AssociationAmerican College of Cardiology valvular heart disease guidelines identify severe aortic stenosis AS. 2 However up to 50 of patients with severe AS are known to have low-gradient AS which is defined as AVA.
ACCAHA 2006 guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease. Various diagnostic modalities are needed to accurately determine the severity of aortic stenosis and potential treatment benefit. Practice Guidelines as Topic.
The occurrence of low-flow low-gradient severe aortic stenosis in patients with normal left ventricle LV ejection fraction has only been recently described. Saeed S Senior R Chahal NS. Inherent inconsistencies in the guidelines criteria prolonged ejection.
So the Low Flow Low gradient severe Ao Stenosis is existing. Authors Eric Awtry 1 Ravin Davidoff. Management of Paradoxical Low-Flow Low-Gradient Aortic Stenosis Need for an Integrated Approach Including Assessment of Symptoms Hypertension and Stenosis Severity.
2015 ESC Guidelines for. Severe aortic stenosis is defined as an aortic valve effective orifice area AVA 10 cm2 or 06 cm2 if indexed for body surface area and a mean transvalvular gradient 40 mmHg. Lowflow lowgradient LFLG aortic stenosis AS is one of the most challenging cardiovascular conditions in terms of diagnosis and therapeutic management.
This article summarizes current guidelines and best practices for the management of. In the Western population prevalence increases exponentially with age resulting in a prevalence of 98 in octogenarians. 815 and guidelines 2 recommend classifying patients with small AVA and preserved LVEF into 4 groups according to their levels offlow ie SVi.
In the American College of CardiologyAmerican Heart Association guidelines the. Different Patterns of Flow Gradient Aortic Stenosis In the American Heart AssociationAmerican College of Cardiology and European Society of CardiologyEuropean Association of Cardiothoracic Surgery guidelines12 severe aortic stenosis AS is defined as a peak aortic jet velocity 40 ms a mean gradient 40 mm Hg or an aortic valve area. Low flow is defined in the guidelines as a stroke volume index gradient is highly flow-dependent ie.
ACCAHA guidelines for the management of patients with valvular heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 2012. Ad Ranked No1 In Heart Vascular Thoracic Care for 27 Years.
Valvular aortic stenosis AS is the most frequently observed valvular heart disease. Paradoxical low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis. Its a complicated entity and the treatment is still debated even if some patients would probably take advantage of the aortic valve replacement.
Intervention is recommended for symptomatic patients with severe high-gradient aortic stenosis or with severe low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis with LVEF 50 and evidence of flow reserve as well as for asymptomatic patients with severe stenosis who have systolic LV dysfunction LVEF 50 without another cause or who have symptoms on. Task force on. A European multicenter study.
Severe AS is defined as peak transvalvular flow velocity 4 ms mean gradient 40 mmHg andor AVA. In this case the mean Gradient is 40 mm Hg so is clear it is a severe aortic stenosis. True-severe classical and paradoxical low.
Article summarizes current guidelines and best practices for the management of low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis. But dont forget the PEDOFF. Summary Low-flow low-gradient aortic stenosis is a difficult entity to diagnose and treat.
CT is recommended in the 2017 edition of the European Guidelines 2 to confirm stenosis severity in LFLG patients with no FR and indication class for AVR has been raised from IIb to. Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis with preserved LVEF. Low flow low gradient aortic stenosis with reduced LVEF.
The purpose of this review is to highlight the diagnostic and management specificities of this entity. Dessa patienter har oftast endast måttlig aortaklaffstenos. The second step is to distinguish pseudo-severe from true severe AS.
AS grading algorithm- an integrated and stepwise approach. A report of the American College of CardiologyAmerican Heart Association. Low-flowlow-gradient aortic stenosis Circulation.
The first step in patients with symptomatic PLF AS should be to rule out measurement errors and treat hypertension. Low-flow Low- gradient LFLG aortic stenosis in patients with a depressed LV ejection fraction.

Complex Scenarios Low Gradient In Low Ef As Patients

Paradoxical Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Circulation

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Dobutamine Stress Echocardiography In Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Flow Reserve Does Not Matter Anymore Journal Of The American Heart Association

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Complex Scenarios Paradoxical Low Gradient As In Normal Patients

Pdf Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Semantic Scholar

Confirmation Of Aortic Stenosis Severity In Case Of Discordance Between Aortic Valve Area And Gradient Sciencedirect

Paradoxical Low Flow Low Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis A Distinct Disease Entity Heart

Pdf Assessment Of Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Multimodality Imaging Is The Key To Success Semantic Scholar

Prognosis Of Severe Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis By Stroke Volume Index And Transvalvular Flow Rate Jacc Cardiovascular Imaging

Evaluation And Management Of The Patient With Low Flow Low Gradient Download Scientific Diagram

Evaluation And Management Of The Patient With Low Flow Low Gradient Download Scientific Diagram

Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis When Is It Severe American College Of Cardiology

Distinction Of Classical And Paradoxical Low Flow Low Gradient Download Scientific Diagram
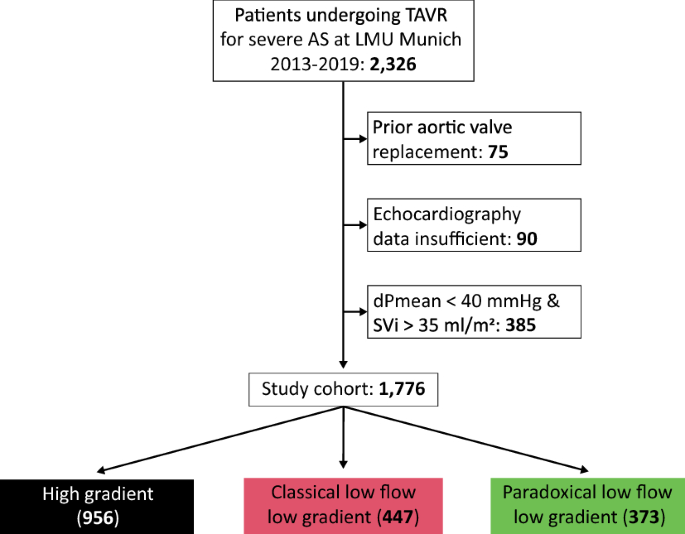
Tavi In Patients With Low Flow Low Gradient Aortic Stenosis Short Term And Long Term Outcomes Springerlink

Simplifying The Approach To Classical Low Flow Low Gradient Severe Aortic Stenosis A Renewed Emphasis On The Resting Transthoracic Echocardiogram International Journal Of Cardiology

Figure Stepwise Approach To The Complex Subgroup Of Low Gradient Download Scientific Diagram